The General Properties show generic properties common to all form field elements.
The Name property identifies the field. Names do not have to be unique, and they are commonly used to access the field object in JavaScript. A common example of JavaScript code that utilizes the field name is shown below.
var field = this.getField("Text1");
Giving form fields the same Name here will result in some specific relationships, depending on the type of field:
Buttons are not affected when they share the same Name and Digital Signature fields are not allowed to share the same Name.
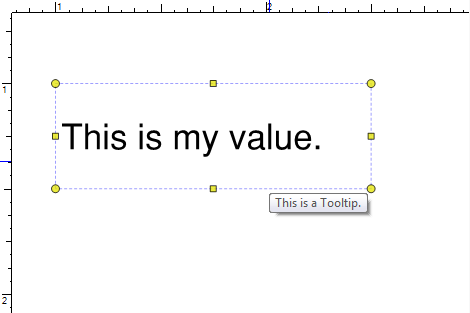
The Tooltip property holds a string of text that appears when the mouse hovers over the field, as illustrated below with the tooltip, “This is a ToolTip”, being shown when the mouse hovers over the field.

The Field property specifies the print and document visibility. Options include:
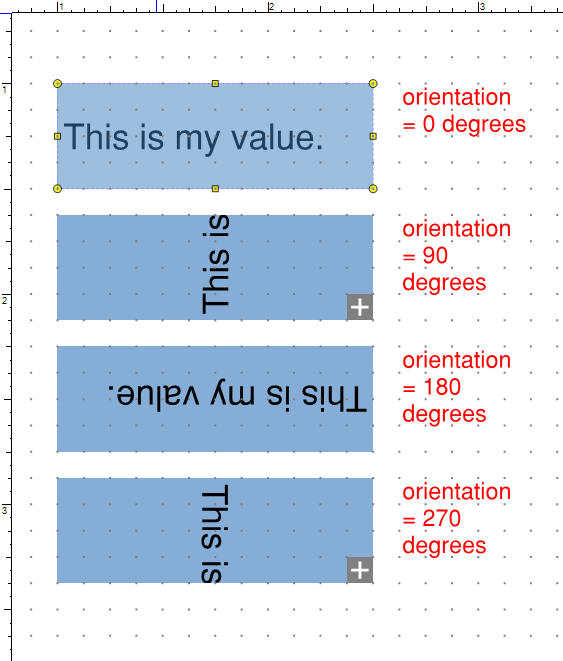
The Orientation property sets the angle at which the contents of the field will be rendered. There are four options: 0 degrees, 90 degrees, 180 degrees, or 270 degrees. An example of a Text Box with the various orientation options is shown below.
The Read-Only property enables/disables further user input; however, dynamic input from JavaScript may still modify the field’s value. Use this option when generating text that is not intended to be modified by the user. The Read-Only property does not affect the position of the form field—in other words, a field can be marked Read-Only and be moved around in the document.
The Required property forces users to specify a value for the field.
The Lock property disables the ability for the user to change a field’s position, style, and other properties. Set the Lock and Read-Only properties together to stop users from making any changes to a field.
The Modified property indicates the time that the field was last modified.